Conditions We Treat
Explore Our Approach
At Halifax Health our physicians are leaders in their fields with the most advanced medical technology at their fingertips and working alongside a highly skilled nursing and professional staff.
Acute Spinal Cord Injury
What is an Acute Spinal Cord Injury?
Your spine is made of many bones called vertebrae. Your spinal cord runs downward through a canal in the center of these bones. The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body for movement and sensation.
Acute spinal cord injury (SCI) is a traumatic injury that bruises, partially or completely tears the spinal cord. SCI is a common cause of permanent disability and death in children and adults.
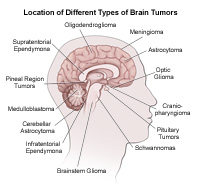
Brain Tumor
What is a Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in the brain.
Types of primary brain tumor
There are 2 types of primary brain tumors:
- Benign tumor. This kind of tumor is not cancer. It tends to grow slowly. Most benign brain tumors don’t grow into nearby tissue. Once removed, they usually don’t grow back. A benign tumor can cause symptoms like a malignant tumor depending on its size and location in the brain.
- Malignant tumor. This kind of tumor is cancer. It usually grows fast, and grows into nearby tissue. This can make it hard to remove fully. A malignant brain tumor may grow back after treatment.
Primary brain tumors are named by the type of brain tissue where they’re found. The most common type of primary brain tumor is a glioma. This type begins in the supportive (glial) tissue of the brain. Some gliomas tend to grow slowly. Others grow and spread quickly. Some types of glioma include:
- Astrocytoma. This kind of tumor comes from small star-shaped cells called astrocytes. In adults, an astrocytoma usually grows in the cerebrum. In children, they can grow in the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. Most astrocytomas spread into nearby normal brain tissue and are hard to cure with surgery. Glioblastoma is a type of astrocytoma that tends to grow very quickly.
- Brain stem glioma. This kind of tumor of the brain stem is more common in children than in adults. Because the brain stem controls many important functions, such as breathing and heart rate, this kind of tumor usually can’t be removed by surgery.
- Ependymoma. This kind of tumor starts in cells that line the fluid-filled spaces within the brain (ventricles). It doesn’t often grow into nearby brain tissue. This means in some cases it can be cured with surgery.
- Oligodendroglioma. This kind of tumor starts in cells that make myelin, the fatty substance that surrounds nerve cells. Like an astrocytoma, this tumor tends to spread into nearby brain tissue and is often hard to cure with surgery.
- Optic nerve glioma. This kind of tumor grows in or around the nerve that sends messages from the eyes to the brain. This can cause vision changes. It can also cause hormone changes, due to its location near the pituitary gland.
Other types of primary tumors include:
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET). This kind of tumor grows more often in children. It can grow anywhere in the brain in the primitive form of nerve cells. One type is the medulloblastoma. This kind of tumor is found in the cerebellum. They are more common in children than in adults. They tend to grow and spread quickly, but they can often be treated effectively.
- Tumor of the pineal gland. This kind of tumor grows in and around the pineal gland. This is a tiny organ near the center of the brain. The tumor can be slow-growing, called pineocytoma. Or it can be fast-growing, called pineoblastoma.
- Pituitary tumor. This kind of tumor starts in the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. It is almost always benign. But it can cause serious symptoms because of its location, and because it may secrete excess hormones.
- Craniopharyngioma. This kind of tumor starts near the pituitary gland. It is usually slow growing. But it can cause symptoms if it presses on the pituitary gland or on nearby nerves.
- Schwannoma. This kind of tumor starts in myelin-making cells that surround certain nerves. It’s most common in the vestibular nerve in the inner ear that helps with balance. If it grows there, the tumor is called a vestibular schwannoma or an acoustic neuroma. This type of tumor is usually benign.
- Meningioma. This kind of tumor starts in the outer linings of the brain (meninges). It is more common in adults. Many meningiomas can be removed with surgery, but some may grow back.
- Primary central nervous system lymphoma. This is an aggressive, rare type of tumor that starts in lymphocytes. This is a type of immune cell. The tumor is more common in people with a disease of the immune system, such as AIDS. But it can grow in healthy people.
Cerebral Abscess
What is a Cerebral Abscess?
A cerebral abscess is a pus-filled pocket of infected material in your brain. It is sometimes called a brain abscess.
An abscess can cause your brain to swell, putting harmful pressure on brain tissue. An abscess can also keep blood from flowing to parts of your brain. If you develop this problem, you will need emergency treatment.
What causes a cerebral abscess?
A cerebral abscess usually occurs when bacteria or fungi make their way into your brain, either through your bloodstream or from an infected area in your head, such as your ears or sinuses. An injury to your head or head surgery can also let in germs that can cause an abscess.
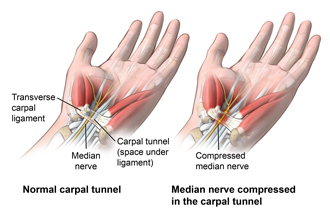
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is when the median nerve is compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is an opening in your wrist that is formed by the carpal bones on the bottom of the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament across the top of the wrist. The median nerve provides sensory and motor functions to the thumb and 3 middle fingers. If it gets compressed or irritated, you may have symptoms.
Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
What is Arteriovenous Malformations
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) happen when a group of blood vessels in your body forms incorrectly. In these malformations, arteries and veins are unusually tangled. This usually happens during development before birth or shortly after.
Most people with AVMs have no initial symptoms or problems. Instead, the AVMs are often discovered when healthcare providers treat another unrelated health concern. Sometimes the rupture of one of the blood vessels in an AVM will bring the issue to medical attention. Sometimes they are only found after death, during an autopsy.
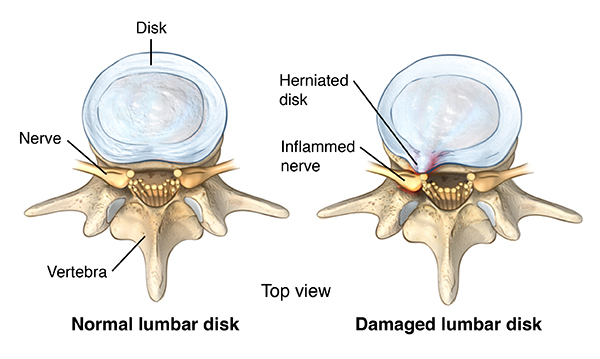
Cervical and Lumbar Herniated Disk
What is a Herniated Disk?
The vertebral column, or backbone, is made up of 33 vertebrae that are separated by spongy disks. The spine is divided into 4 areas:
- Cervical spine: The first 7 vertebrae, located in the neck
- Thoracic spine: The next 12 vertebrae, located in the chest area
- Lumbar spine: The next 5 vertebrae, located in the lower back
- Sacral spine: The lowest 5 vertebrae, located below the waist, also includes the 4 vertebrae that make up the tailbone (coccyx)
The lumbar spine consists of 5 bony segments in the lower back area, which is where lumbar disk disease occurs.
- Bulging disk. With age, the intervertebral disk may lose fluid and become dried out. As this happens, the spongy disk (which is located between the bony parts of the spine and acts as a “shock absorber”) becomes compressed. This may lead to the breakdown of the tough outer ring. This lets the nucleus, or the inside of the ring, to bulge out. This is called a bulging disk.
- Ruptured or herniated disk. As the disk continues to break down, or with continued stress on the spine, the inner nucleus pulposus may actually rupture out from the annulus. This is a ruptured, or herniated, disk. The fragments of disc material can then press on the nerve roots located just behind the disk space. This can cause pain, weakness, numbness, or changes in sensation.
Most disk herniations happen in the lower lumbar spine, especially between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae and between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the first sacral vertebra (the L4-5 and L5-S1 levels).
Chiari Malformation
What is a Chiari Malformation?
A Chiari malformation is a problem in which a part of the brain (the cerebellum) at the back of the skull bulges through a normal opening in the skull where it joins the spinal canal. This puts pressure on parts of the brain and spinal cord, and can cause mild to severe symptoms. In most cases, the problem is present at birth (congenital).
There are several types of Chiari malformations, but type I is the most common. In type I, the cerebellum bulges through the normal opening at the base of the skull. This type is most often congenital. It is also called primary Chiari malformation type I. But it is often not found until a person is a teen or young adult.
In rare cases, this type may also develop later in life. This is known as acquired or secondary Chiari malformation type I.
Craniopharyngioma
What is Craniopharyngiomas?
A craniopharyngioma is a benign tumor that is found near the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is under the brain but directly connected to it. It controls the production of many hormones in the body.
A craniopharyngioma is usually a mixture of both solid tissue and fluid-filled cysts. The tumor is not cancer. It does not spread to other parts of the body. But as it grows, it may press on parts of the brain and nearby tissue. This affects hormones, vision, and other normal functions. For this reason, it needs to be treated. This kind of tumor is most often found in boys and girls 5 to 14 years old.
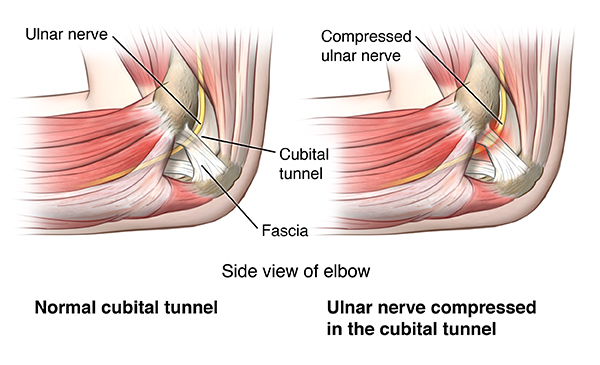
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
What is Cubital Tunnel Syndrome?
Cubital tunnel syndrome happens when the ulnar nerve, which passes through the cubital tunnel (a tunnel of muscle, ligament, and bone) on the inside of the elbow, is injured and becomes inflamed, swollen, and irritated.
Cubital tunnel syndrome causes pain that feels a lot like the pain you feel when you hit the “funny bone” in your elbow. The “funny bone” in the elbow is actually the ulnar nerve, a nerve that crosses the elbow. The ulnar nerve begins in the side of your neck and ends in your fingers.
Hemifacial Spasm
What is a Hemifacial Spasm?
Hemifacial spasm is a nervous system disorder in which the muscles on one side of your face twitch involuntarily. Hemifacial spasm is most often caused by a blood vessel touching a facial nerve, but it may be caused by a facial nerve injury or a tumor, or it may not have a cause.
Hydrocephalus
What is Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus?
The brain has chambers called ventricles that normally contain fluid. This fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It cushions the brain and spinal cord. Normally your body makes just enough CSF each day and absorbs that same amount. Sometimes, however, too much fluid can build up in the ventricles. This can lead to a normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH).
Kyphosis Deformities
What is Kyphosis?
A normal spine, when viewed from behind appears straight. However, a spine affected by kyphosis has a forward curvature of the back bones (vertebrae) in the upper back area, giving an abnormally rounded or “humpback” appearance.
Kyphosis is defined as a curvature of the spine measuring 50 degrees or greater on an X-ray. The normal spine can bend from 20 to 45 degrees of curvature in the upper back area. Kyphosis is a type of spinal deformity.
Metastatic brain tumor
What are Metastatic Brain Tumors?
Sometimes tumors growing in the brain begin there. These are called primary brain tumors. But other types of brain tumors begin as cancers somewhere else in the body. These can start in the lung, breast, skin, kidney, colon, or other body parts. They may spread to the brain even if the cancers are controlled at the original site. These are called secondary or metastatic brain tumors.
In adults, metastatic brain tumors are more common than tumors that begin in the brain. They are also treated differently from those that start in the brain.
Facts about metastatic brain tumors
Cancer may spread to the brain through your lymph system or your bloodstream. Or it may travel to the brain from a nearby tissue. Metastatic brain tumors are becoming more common because people are living longer after having cancer somewhere else in their body.
In most cases, the metastatic brain tumor is found in the cerebrum. This is the outer part of the brain that controls your thoughts, emotions, and language ability. It also is involved in movement and sensing the outside world. But metastasis can appear in other areas of the brain, too.
Metastatic brain tumors happen most often in lung cancer. But these tumors can occur in many other types of cancer, such as melanoma or breast cancer.
Rathke Cleft Cysts
What are Rathke Cleft Cysts?
Rathke cleft cysts (RCCs) are benign (non-cancerous) fluid-filled growths that develop between the parts of the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. They are congenital deformities, meaning that they develop while a fetus is growing in the womb. An RCC develops from a piece of the fetus’ developing Rathke pouch, which ultimately becomes part of the pituitary gland.
Rathke cleft cysts are rare. And, they rarely cause symptoms or problems during childhood, so they are not usually diagnosed in kids. Rather, they are most often found in adults during an MRI scan to diagnose another problem, or even after death, if an autopsy is done. Women are more likely to develop this condition compared to men.
If Rathke cleft cysts become large enough, they can cause vision changes or various problems with the pituitary gland’s normal processes.
Spinal Cord Tumors
What are Spinal Cord Tumors?
A tumor forms when an abnormal cell grows to form a mass of abnormal cells. Spinal cord tumors are tumors that form in the spinal cord or in the area around it.
A spinal cord tumor may be cancer (malignant) or noncancer (benign). A benign tumor can often cause pain and discomfort because it pushes on the spinal cord or nerves.
A spinal cord tumor may be called primary. This means the cancer started in the spinal cord. Or the tumor may be secondary. This means the cancer started somewhere else in the body and spread to the spinal cord. Most of the time, spinal cord tumors are secondary tumors. A spinal cord tumor is often a cancer of the lung, breast, prostate, or another cancer that has spread throughout the body to reach the spine.
Spinal cord tumors are sometimes caused by a genetic disorder, such as neurofibromatosis.
Scoliosis Deformities
What is Scoliosis?
A normal spine, when viewed from behind, appears straight. However, a spine affected by scoliosis shows a side-to-side curvature, with the spine looking like an “S” or “C.” The back bones (vertebrae) may also be rotated. This makes it look like the person is leaning to one side. Scoliosis is defined as a curvature of the spine measuring 10° or greater.
Scoliosis is not due to poor posture.
Spinal curvature from scoliosis may occur on the right, left or both sides of the spine. Both the thoracic (mid) and lumbar (lower) spine may be affected by scoliosis.
Traumatic Brain Injury
What is a traumatic brain injury?
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a type of brain injury caused by a blow or jolt to, or penetration of the head. A TBI can occur during a car accident, from being tackled during a football game, or from a combat-related wound.
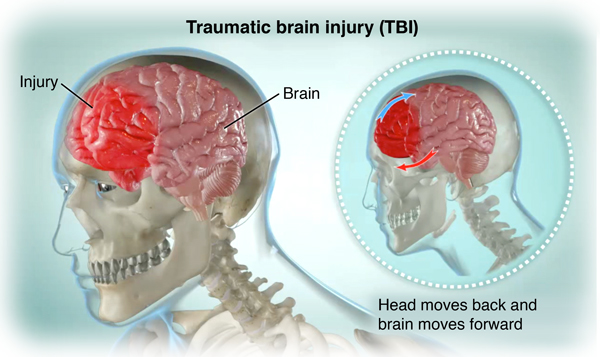
After a TBI, nerve cells in the brain may be damaged. The neurons may have trouble doing their job of carrying signals to different parts of the brain. If you have a brain injury, you could have trouble thinking or moving normally. Your brain may also have trouble keeping your body working properly.
Most cases of brain injury that occur each year are mild. A concussion is a minor form of brain injury. But, many TBIs can be severe. Severe brain injuries require emergency care. People with severe injuries may require a lengthy recovery period, and their symptoms can linger for a long time.
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a type of nerve pain that affects your face. You may feel a strong burst of pain in part of your face. It is usually on one side of the jaw or cheek. The pain may be burning or sharp, and so severe that you can’t eat or drink.
A flare-up begins with tingling or numbness in the area. Then pain starts to come and go, often in bursts that last anywhere from a few seconds to 2 minutes. During a flare of the condition, these bursts of pain may become more and more frequent until the pain almost never stops. The intensity of the pain can make it hard to get through your day. But it’s not life-threatening.
This chronic pain condition can flare up for a few weeks or months. Then the pain goes away for a while, sometimes years.